
Understanding GDPR and Its Core Principles
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is one of the most significant data privacy laws established by the European Union to protect the rights of individuals regarding their personal information. It applies not only to businesses within the EU but also to organizations outside of it if they collect or process data from EU citizens. This law emphasizes transparency, accountability, and responsibility, requiring companies to handle personal data with the highest level of security and fairness. For organizations using visitor management systems, GDPR creates a structured framework that ensures visitor data is collected, stored, and processed lawfully.
The core principles of GDPR—lawfulness, fairness, transparency, purpose limitation, data minimization, accuracy, storage limitation, and integrity—directly affect how visitor information is managed. For example, when visitors sign in at corporate offices or public facilities, their data must be collected only for necessary purposes and stored for a limited duration. Companies must also make this process clear to the visitors by providing information on why their data is being collected and how it will be used. Failure to follow these principles can result in reputational damage and severe legal consequences.
By aligning visitor management practices with GDPR principles, organizations demonstrate a commitment to respecting individual privacy rights while fostering trust among their clients, employees, and partners. Compliance is not just about meeting legal requirements; it is about building credibility in an age where personal information is increasingly vulnerable to misuse. Companies that prioritize GDPR compliance set themselves apart as trustworthy custodians of data in an environment where security breaches can be highly damaging
The Role of Visitor Management Systems in Data Privacy
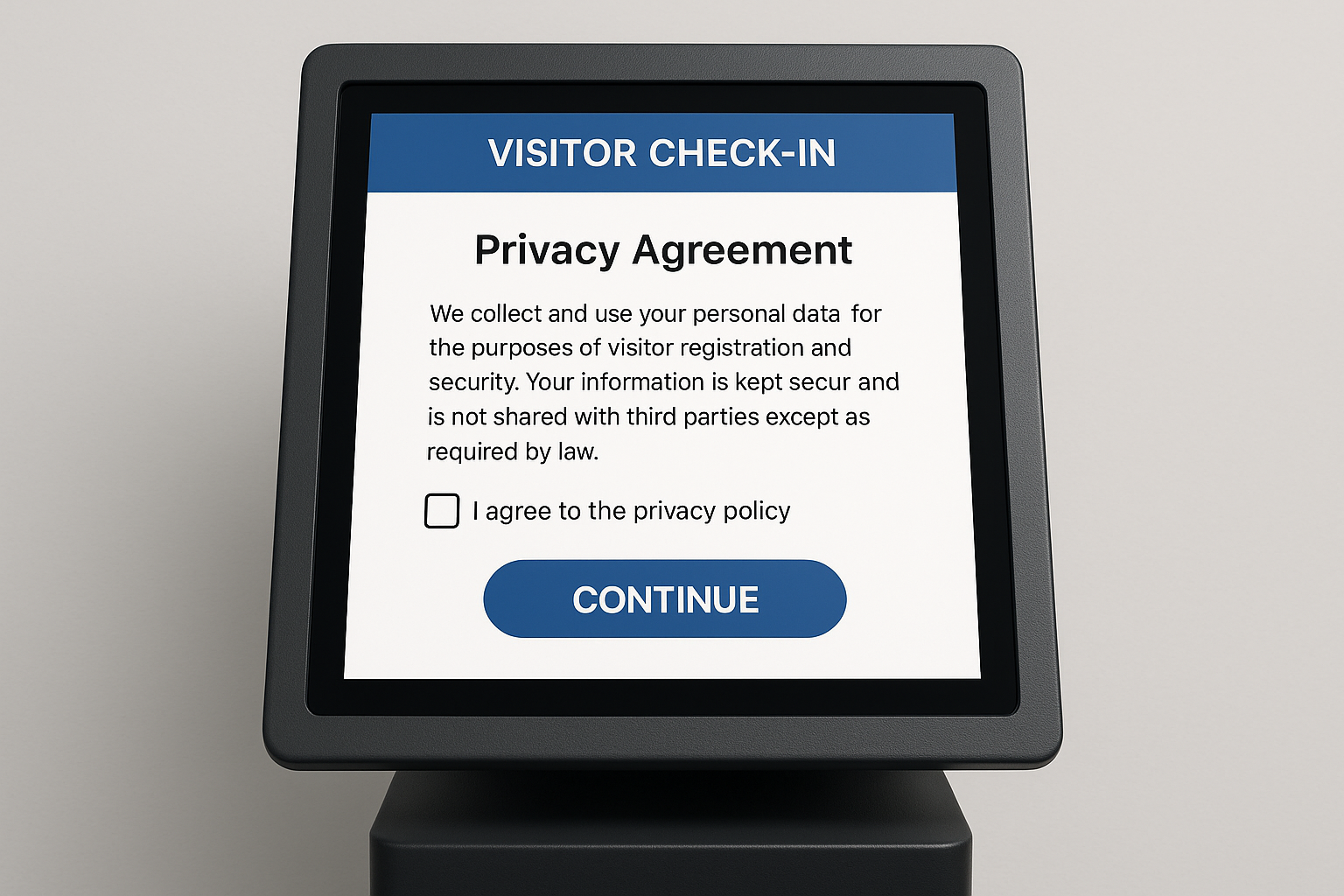
Modern visitor management systems (VMS) play a vital role in ensuring that personal information is safeguarded from the moment a visitor enters a building. Unlike traditional paper-based logbooks, which can easily expose sensitive details to unauthorized individuals, digital systems provide encrypted storage and controlled access. This helps organizations meet GDPR requirements by reducing the risk of unauthorized data exposure. For instance, visitor data such as names, identification documents, or contact details can be securely stored and automatically deleted after the retention period ends.
These systems also offer customizable consent options, enabling organizations to capture visitor approval for data collection in a transparent and compliant manner. Visitors can be presented with digital agreements or privacy notices before they sign in, ensuring that they are fully aware of how their information will be used. This type of functionality not only ensures compliance but also provides peace of mind to visitors, who increasingly value transparency when it comes to their personal data.
Additionally, advanced VMS solutions integrate access control features that ensure only authorized personnel can view or manage visitor data. Audit trails and reporting functions make it possible for organizations to track who accessed certain information and when, providing accountability and compliance verification. This makes visitor management systems indispensable tools in aligning operational efficiency with strict data privacy requirements.
Consequences of Non-Compliance and the Path Forward

Failing to comply with GDPR can have significant financial, legal, and reputational consequences for organizations. The law allows for fines of up to €20 million or 4% of annual global turnover, whichever is higher, depending on the severity of the violation. Beyond financial penalties, non-compliance can erode customer trust and damage brand reputation, particularly in industries where data privacy is a top priority. For visitor management, even a small breach—such as leaving visitor logs exposed—can escalate into a compliance issue that undermines organizational credibility.
To avoid such risks, organizations must take proactive measures in ensuring GDPR compliance within their visitor management practices. This includes conducting regular audits of how visitor data is collected, stored, and deleted, as well as training staff to handle sensitive information responsibly. Deploying technology that supports GDPR principles is a vital step, but organizations must also cultivate a culture of data privacy, where employees and stakeholders understand the importance of safeguarding personal information.
Looking ahead, GDPR compliance in visitor management will continue to evolve as digital systems advance and regulations expand. Organizations that remain committed to compliance will not only avoid penalties but will also position themselves as leaders in data security and privacy. In an era where personal data is one of the most valuable assets, demonstrating care and responsibility in handling it will remain a crucial part of building sustainable trust with visitors and clients alike.
RELATED POSTS

Protecting Visitor Data with Secure Digital Platforms
In an age where every visitor interaction generates digital data, organizations face growing pressure to ensure that privacy remains a top priority. From corporate offices and residential complexes to healthcare institutions and government buildings, visitor...
